can dka cause heart attack Ketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
Hey there! Today, I want to talk about a condition called Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA). It’s a serious complication that can occur in people with diabetes, and it’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms.
Hyperglycemia DKA (Ketoacidosis) & Ketones - Diabetes - Innovation
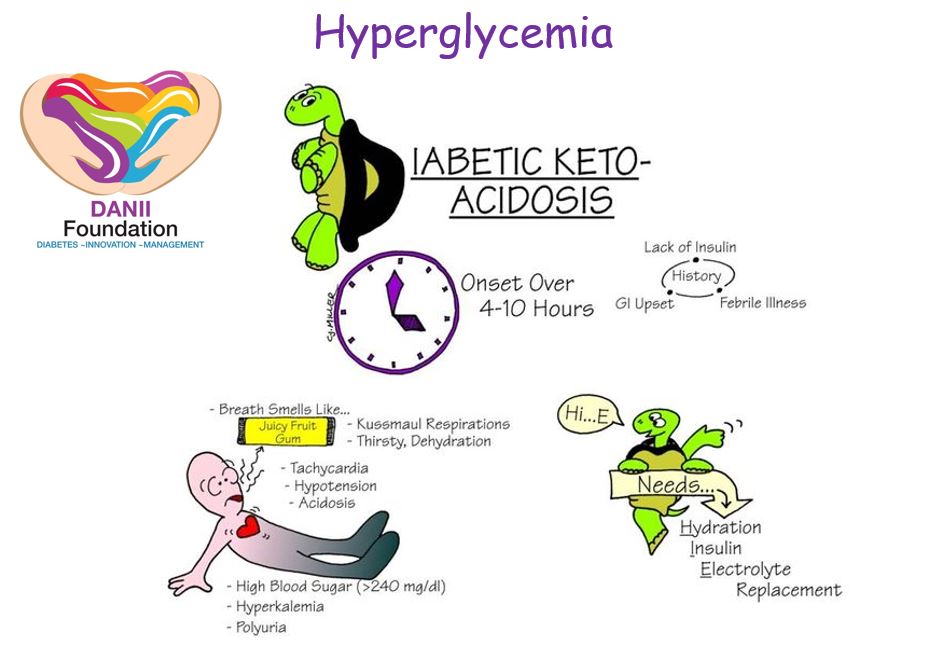 The first image we have here provides some insight into the link between hyperglycemia and DKA. DKA occurs when blood sugar levels rise too high, causing a dangerous imbalance in the body. This can happen when insulin levels are too low, often due to issues with insulin production or utilization in people with diabetes.
The first image we have here provides some insight into the link between hyperglycemia and DKA. DKA occurs when blood sugar levels rise too high, causing a dangerous imbalance in the body. This can happen when insulin levels are too low, often due to issues with insulin production or utilization in people with diabetes.
When the body doesn’t have enough insulin to break down glucose for energy, it starts breaking down fat instead. This process leads to the release of ketones, which can cause acidity in the blood and lead to the development of DKA.
It’s important to note that DKA is more commonly seen in people with type 1 diabetes. However, it can also occur in individuals with type 2 diabetes, especially in certain situations, such as during an illness or infection.
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow
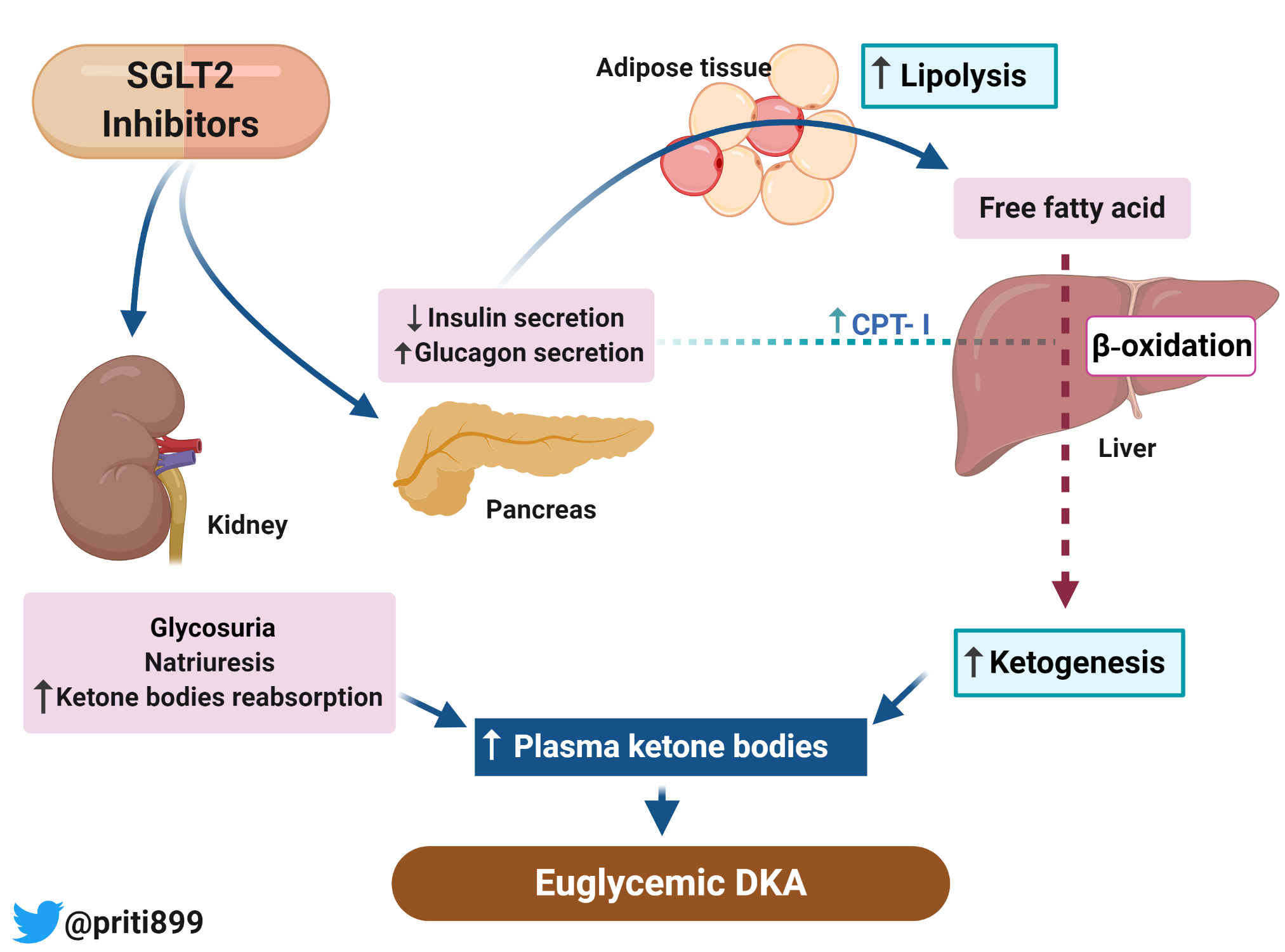 Now, let’s shift our focus to another interesting aspect of DKA. The second image highlights a specific type of DKA called SGLT2 inhibitor-induced euglycemic DKA. This condition occurs in individuals who are taking a class of medications called sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
Now, let’s shift our focus to another interesting aspect of DKA. The second image highlights a specific type of DKA called SGLT2 inhibitor-induced euglycemic DKA. This condition occurs in individuals who are taking a class of medications called sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
SGLT2 inhibitors are commonly prescribed to people with type 2 diabetes to help lower blood sugar levels. However, in some rare cases, these medications can increase the risk of developing euglycemic DKA. Euglycemic DKA refers to a state of DKA where blood sugar levels are not significantly elevated.
It’s important for individuals taking SGLT2 inhibitors to be aware of the signs and symptoms of euglycemic DKA, even if their blood sugar levels appear to be within the normal range. Symptoms can include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, and fruity-smelling breath.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately, as euglycemic DKA can be life-threatening if left untreated.
So, there you have it - a brief overview of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and its different manifestations. Remember, it’s always important to monitor your blood sugar levels closely, take your medications as prescribed, and seek medical advice if you experience any concerning symptoms.
If you are searching about SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Images about SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow like Hyperglycemia DKA (Ketoacidosis) & Ketones - Diabetes - Innovation, SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow and also Heart Attack: Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis - heartathon.com. Here you go:
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow
 www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
Heart Attack: Symptoms, Causes, And Diagnosis - Heartathon.com
 heartathon.comdiagnosis
heartathon.comdiagnosis
DKA In Type 2 Diabetes - PatientEducationMD
 patienteducationmd.comdka diabetes insulin stress lack
patienteducationmd.comdka diabetes insulin stress lack
Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis / Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka
 sraytguh.blogspot.comdiabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology dka starvation jbs elsevierhealth els acidosis correction
sraytguh.blogspot.comdiabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology dka starvation jbs elsevierhealth els acidosis correction
Hyperglycemia DKA (Ketoacidosis) & Ketones - Diabetes - Innovation
 danii.org.auketoacidosis dka diabetic hyperglycemia ketones lead coma death danii hypo serious passing condition au cycle
danii.org.auketoacidosis dka diabetic hyperglycemia ketones lead coma death danii hypo serious passing condition au cycle
Hyperglycemia dka (ketoacidosis) & ketones. Ketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow. Heart attack: symptoms, causes, and diagnosis